

Do you consider yourself a person with good reflexes? Do you want to check it in a fun way? Then you are in the right place. Here we present you the F1 reflex test, an exciting way to test your reaction skills.
In this test, you will have to demonstrate how quickly you react to different visual signals. From flashing lights to moving figures, the F1 reflex test will keep you on your toes and constantly challenged.
Do not miss the opportunity to know your reaction time and have fun at the same time. Read on to find out more about the F1 reflex test and how you can put your skills to the test.
What are reflexes and how do they work?
Reflexes are automatic and involuntary responses of the body to a stimulus. These stimuli can be internal or external and are processed by the central nervous system, which makes it possible for responses to occur without the conscious intervention of the individual. Reflexes are aimed at protecting the body from injury and maintaining its balance.
reflexes anatomy
Reflexes are formed by a reflex arc, which involves a sensory receptor, an afferent nerve, an information processing center in the central nervous system, an efferent nerve, and an effector muscle or organ. The sensory receptor receives the stimulus, which is sent via the afferent nerve to the information processing center in the central nervous system. The information is then processed and a signal is sent through the efferent nerve to the effector muscle or organ, producing the corresponding reflex response.
How reflexes work
Reflexes are produced thanks to the connection between different neurons. Sensory information is processed in the central nervous system, producing a reflex response that is sent to the target muscle or organ. In the case of more complex reflexes, such as those involved in balance and posture, the participation of a greater number of brain structures is required.
Types of reflexes in the human body

There are several types of reflexes in the human body, which can be evaluated to determine the neurological function of the individual. Some of the main types of reflections are described below:
muscle stretch reflex
The muscle stretch reflex is the best known and occurs when a muscle is stretched. This reflex is involuntary and occurs automatically. When a muscle is stretched, sensory receptors located in the tendons send a signal to the central nervous system, causing a reflex contraction in the muscle. This reflex is important to maintain balance and posture, as well as to prevent muscle injury during exercise.
skin flexion reflex
The cutaneous flexion reflex is activated when the skin of a part of the body is stimulated. This reflex can be assessed by applying a painful stimulus, such as a prick with a needle. Under normal conditions, the response to this stimulus is an involuntary contraction of the muscles in the affected area. This reflex is important for neurological evaluation, as it can indicate the presence of lesions in the spinal cord or peripheral nervous system.
Babinski reflex
The Babinski reflex is a pathological reflex that occurs when the sole of the foot is scratched. Under normal conditions, the response is a downward flexion of the foot. However, in some neurological conditions, such as spinal cord injuries, this reflex can be abnormal, causing upward extension of the big toe and abduction of the other toes. This reflex may indicate the presence of a neurological lesion and is important in neurological evaluation.
Tests to Evaluate Reflexes
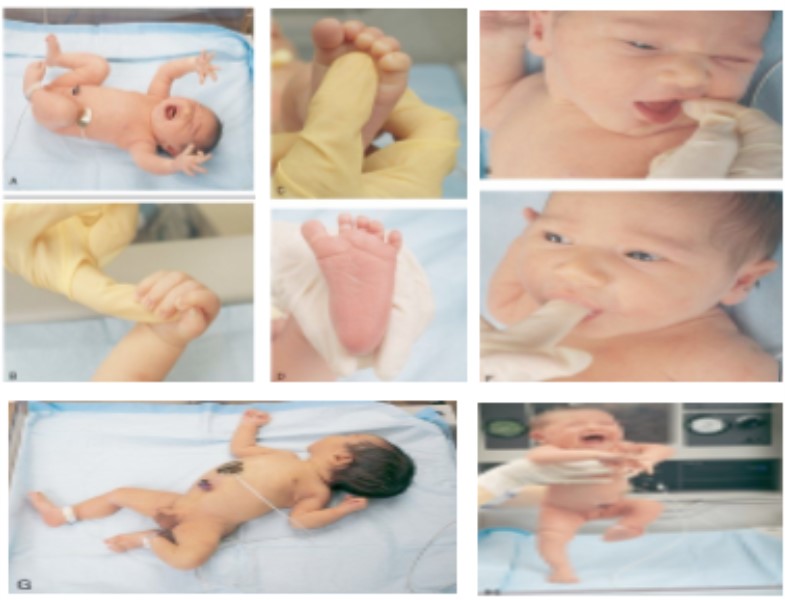
Reflex tests are used by health professionals to assess the nervous system and detect certain injuries or diseases. These tests measure the speed and precision with which reflexes occur in response to a stimulus. Some of the most common tests are described below:
patellar reflex
The knee jerk is one of the best known reflexes and consists of tapping the quadriceps muscle tendon in the knee gently with a rubber hammer, causing the leg to extend involuntarily. A normal response should be a contraction of the quadriceps muscle and extension of the leg. An exaggerated or absent response may be a sign of neurological injury or disease.
Babinski reflex
In the Babinski reflex, the doctor uses an object to scratch the patient’s foot from the heel to the tip of the big toe. In a normal response, the toes should be flexed downward. In an abnormal response, the fingers will move upwards, which could be a sign of central nervous system injury or disease.
Eye defense reflex
The eye defense reflex is designed to protect the eyes from foreign objects. The doctor uses an object, such as a piece of cotton, to gently touch the corner of the patient’s eye. The normal response is involuntary closure of the eye. A slow or absent response may be an indication of facial nerve damage.
What is the F1 reflex test?
The F1 reflex test is a neurological test that evaluates the response of reflexes in the human body. It consists of tapping gently with a reflex hammer on certain areas of the body, such as the knee, ankle, or elbow, and observing the muscle response and reflex speed.
4. How is the F1 reflex test performed?
The F1 reflex test is performed between people sitting in a comfortable position with their legs extended. The examiner holds the foot in one hand and the hammer in the other hand. The tendon area of the knee is gently tapped with the hammer and the response of the leg is observed. The blow must be light enough not to cause pain or damage, but strong enough to elicit a reflex response.
4. What is the objective of the F1 reflex test?
The objective of the F1 reflex test is to assess the integrity of the nervous system and the body’s ability to respond appropriately to external stimuli. It can also help detect early signs of neurological problems, such as multiple sclerosis, Guillain-Barré syndrome, or peripheral neuropathy. The F1 reflex test is a quick, simple, and non-invasive test that can be performed in any clinical setting to assess a patient’s neurological status.
Interpretation of the results of the F1 reflex test
The F1 reflex test is a useful tool in neurological evaluation. The results obtained from the test provide information on the function of the nervous system and its ability to respond to stimuli.
normal results
A normal result of the F1 reflex test is characterized by a rapid and coordinated response of the muscle to stimulation. The muscle response is uniform and consistent. The latency time is short and the amplitude of the reflex is adequate. These results indicate adequate neurological function.
Abnormalities in the results
An abnormality in muscle response may indicate neurological dysfunction. If the latency time is prolonged, it may indicate a peripheral neuropathy or motor neuron disease. If the amplitude of the reflex is low, it may be an indicator of muscle injury or of the neurological pathway. If the muscle does not respond at all, it suggests a serious injury or impaired reflex.
It is important to remember that the results of the F1 reflex test must be interpreted by a qualified health professional. This complete neurological evaluation is necessary to determine the diagnosis and the appropriate treatment plan.
Importance of the F1 reflex test in neurological evaluation
The F1 reflex test is a tool important in the neurological evaluation of patients. This test measures nerve conduction velocity and the integrity of the motor and sensory pathways. The measurement of reflexes using this test is an objective way of evaluating the patient’s neurological function.
Indications of the F1 reflex test
The F1 reflex test is used to evaluate patients with suspected neuromuscular diseases, such as peripheral neuropathies, myopathies, or multiple sclerosis. It is also used to evaluate systemic diseases such as diabetes, where damage to peripheral nerves can cause loss of reflexes.
F1 reflex test procedure
The F1 reflex test procedure consists of applying an electrical stimulus to the skin using electrodes. This stimulus produces a reflex response that is measured by an electromyograph. The results are compared with reference values and the nerve conduction velocity is determined.
In conclusion, the F1 reflex test is an essential tool in the neurological evaluation of patients with neuromuscular or systemic diseases. The measurement of reflexes using this test allows an objective assessment of the patient’s neurological function, allowing for more accurate and effective treatment.
How to improve reflexes and prevent injuries
In addition to evaluating reflexes, it is important to work on improving them and preventing injuries. Some tips and exercises to achieve this are:
Activities that stimulate coordination and balance
Activities like yoga, tai chi, and dance can help improve coordination and balance, which in turn can improve reflexes. These exercises can also help prevent injury by improving stability and body control.
Agility and reaction exercises
Agility and reaction drills can help improve response times and quick reflexes. Exercises such as hopping on one foot or throwing and catching a ball can be helpful in improving reflexes.
Balanced diet and adequate rest
Maintaining a balanced diet and getting enough sleep is essential to maintain proper functioning of the nervous and muscular systems. This can contribute to a quick and effective reflex response and prevent injury.
In summary, it is important to evaluate the reflexes to detect possible neurological problems, but it is also essential to improve them and prevent injuries through healthy lifestyle habits and specific exercises.
